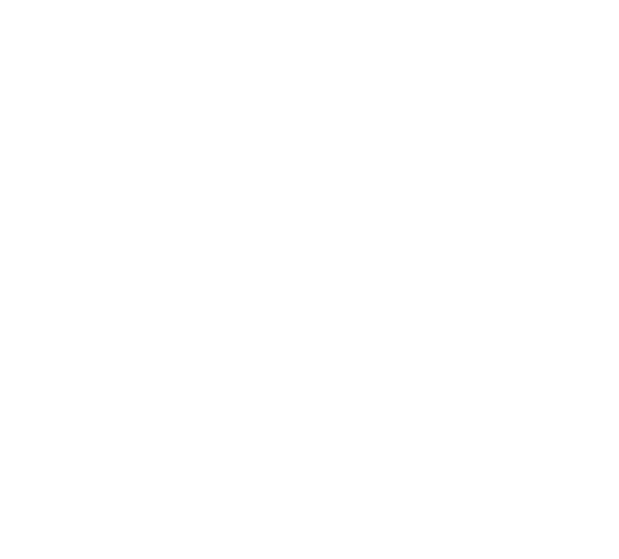
| TLDR
Most businesses want to reduce plastic use, but cost, performance, and consumer acceptance are real hurdles. This blog simplifies the process by highlighting 8 eco-friendly packaging materials that are practical, scalable, and sustainable. Packaging falls under three key layers: primary (product-facing), secondary (grouping), and tertiary (shipping). The 8 sustainable packaging types include:Corrugated Cardboard – Recyclable, sturdy, great for shipping. Compostable Bioplastics (PLA+PBAT) – Durable and CPCB-certified for India’s waste systems. Water-Activated Tape – Eco-friendly sealing, recyclable with boxes.Organic Cotton & Jute Bags – Long-lasting, reusable alternatives to plastic. Corrugated Bubble Wrap – Cushioning protection without plastic.Mushroom Packaging – Biodegradable, shock-resistant, and futuristic. Greenworksbio helps businesses shift with CPCB-certified, customisable, compostable packaging built for Indian systems. Choose packaging that reduces waste and supports brand sustainability. |
|---|
Many businesses struggle to find packaging that’s strong, eco‑friendly, affordable, and scalable—all at once. A 2024 survey of 300 senior leaders in European food and drink companies found that 98% are committed to reducing plastic packaging, yet 40% cite raw material costs as their biggest barrier, and 72% fear consumers won’t pay extra for sustainable options. These challenges highlight how tough it is to balance performance, cost, and consumer expectations.
That’s exactly where this blog helps. We’ve simplified the process by breaking down 8 types of packaging products and various kinds of packaging materials that are not only practical and reliable but also reduce your environmental impact. Whether you’re shipping, displaying, or protecting your product, you’ll find solutions that align with both performance goals and sustainability standards, without compromising either.
What are the 3 Categories of Packaging?
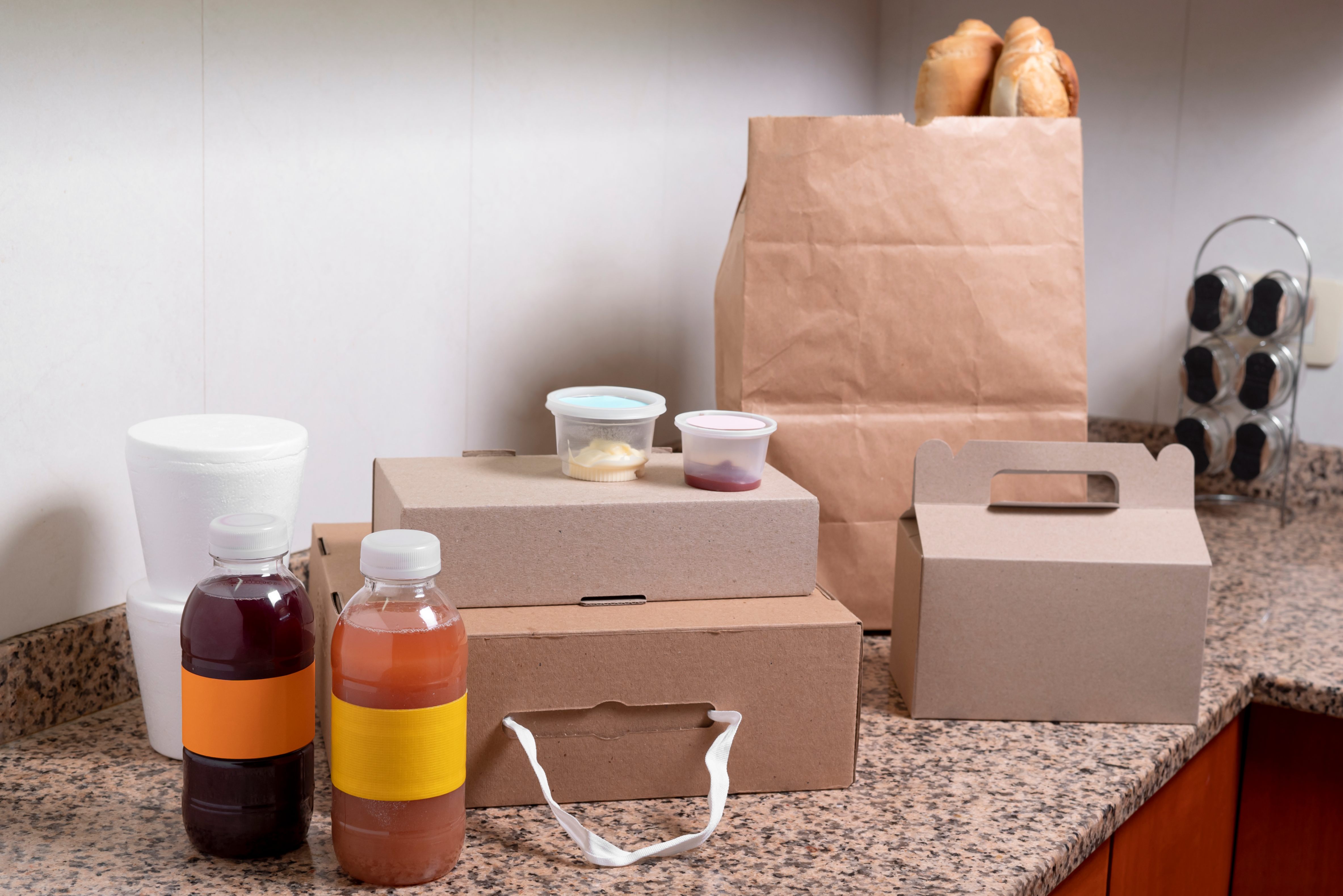

Before diving into material types, it’s important to understand how packaging is structured across the supply chain:
1. What Is Primary Packaging?
This is the first layer of protection and comes in direct contact with the product. It’s what consumers see and handle first—like a juice bottle, a biscuit wrapper, or a cosmetic tube. Primary packaging, with its ease of use, keeps the product fresh, safe, and usable while often displaying key information like ingredients, instructions, or expiry dates. Different products require primary packaging that plays a vital role in being crucial for both functionality and first impressions, influencing the type of material used.
2. How Does Secondary Packaging Impact Eco-Friendly Practices?
This layer holds together different types of products (multiple units), ultimately delivering them to the end user. Think of the cardboard box holding six tubes of toothpaste or the paper sleeve around a set of jars. Secondary packaging adds additional protection while supporting bulk handling, branding, and retail display. It also helps during storage and makes transport easier while offering a canvas for logos, visuals, and product details.
3. What Role Does Tertiary Packaging Play in a Greener Supply Chain?
Used mainly for shipping and large-scale distribution, tertiary packaging, including packaging supplies, encompasses materials like stretch-wrapped pallets, corrugated cartons, and other common packaging materials like plastic crates and heavy-duty crates that come in different shapes. It ensures that goods remain stable and protected during long-haul transport and warehouse stacking. Though invisible to consumers, this layer is key for operational efficiency and minimising transit damage.
What Are 8 Must-Know Types of Packaging Materials?
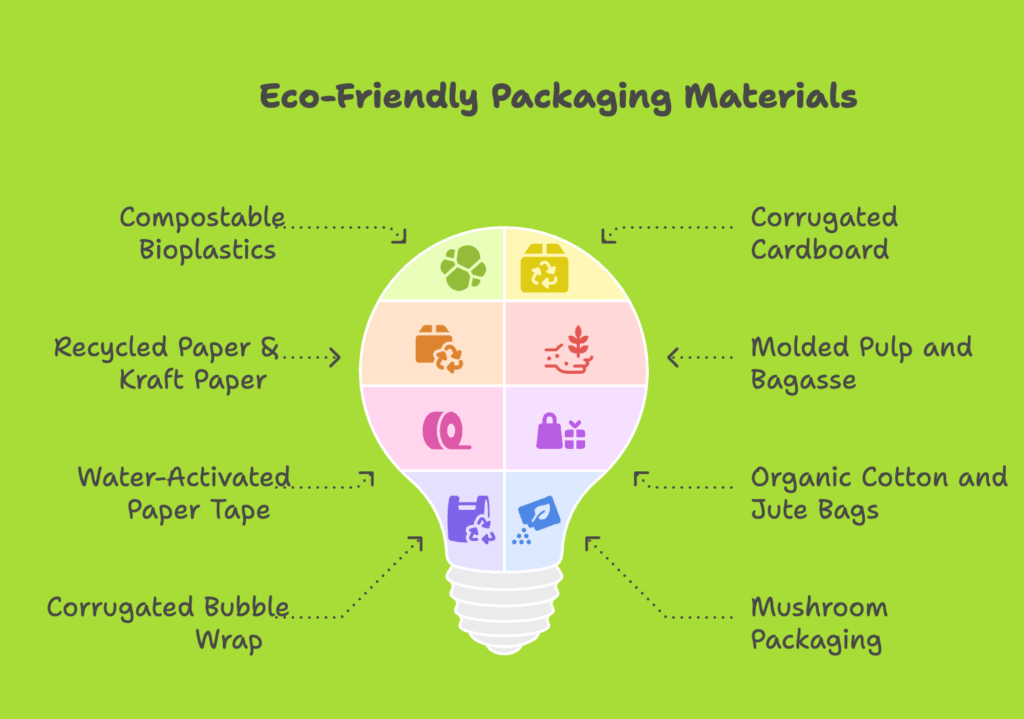
Choosing the right packaging—like paper pulp—helps balance sustainability with functionality. We’ll explore the top eco-friendly options below to help you choose what fits best.
1. Compostable Bioplastics (PLA+PBAT)

Bioplastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) blended with PBAT (Polybutylene adipate terephthalate) are made from renewable sources such as corn starch or sugarcane. They offer the convenience of plastic but are compostable under industrial conditions, typically within 90–180 days.
- Common Uses: Courier bags, food containers, cutlery, and wrappers in different sizes.
- Why It Works: Food-safe, flexible, durable, and suitable for Indian composting infrastructure
- Certifications to Look For: CPCB (India), EN 13432, ASTM D6400, TÜV Austria
- Important Note: Avoid petroleum-blended versions; always check for certified compostability
Check out the Greenworksbio product collection for sustainable packaging products
2. Corrugated Cardboard
Corrugated cardboard is one of the most widely used and trusted packaging materials. Made by sandwiching fluted paper between flat layers, it provides excellent structural strength while staying lightweight. It’s especially useful for protecting products during shipping and handling and is recognized as a widely used packaging solution.
- Common Uses: Shipping boxes, eCommerce cartons, product display boxes
- Why It Works: Strong, reusable, and recyclable; ideal for secondary and tertiary packaging
- Sustainability Tip: Choose FSC-certified cardboard or ones made from post-consumer waste to support responsible sourcing and recycling
3. Recycled Paper & Kraft Paper
Recycled and kraft paper are biodegradable and widely used for sustainable packaging. They are typically made from post-consumer or agricultural waste pulp and are free of harmful chemical treatments.
- Common Uses: Wrapping paper, paper bags, fillers, labels, sleeves
- Why It Works: Lightweight, easily recyclable, and cost-effective
- Ideal For: Brands looking for rustic, minimal, or organic packaging aesthetics
- Tip: FSC or PCW (post-consumer waste) labels indicate ethical sourcing
4. Molded Pulp and Bagasse
Bagasse is a byproduct of sugarcane juice extraction, while molded pulp is formed from recycled paper. Both materials are compostable and naturally degrade without leaving toxic residues. They also insulate heat and absorb shock, making them perfect for sensitive items.
- Common Uses: Egg trays, meal boxes, clamshell containers, electronics holders
- Why It Works: Strong yet lightweight; biodegradable and food-grade
- Great For: Takeaways, bakeries, electronics packaging, and sustainable gifting
5. Water-Activated Paper Tape
This eco-friendly alternative to plastic tapes is made from kraft paper and uses a starch-based adhesive. The tape activates when moistened and bonds strongly with corrugated surfaces.
- Common Uses: Sealing cartons, shipping boxes
- Why It Works: Fully recyclable along with cardboard—no need to remove before recycling
- Bonus Point: Can be custom printed for brand visibility and a premium unboxing experience
6. Organic Cotton and Jute Bags
Unlike plastic bags, organic cotton and jute are reusable, natural fibre alternatives. These materials, including plastic containers, are grown without pesticides and processed using eco-friendly methods, making them a responsible packaging choice alongside wooden boxes and plastic trays.
- Common Uses: Tote bags, grocery bags, product sacks, gift bags
- Why It Works: Long-lasting, biodegradable, and recyclable
- Sustainability Note: Cotton uses less water than synthetic fabrics and jute is entirely rain-fed—great for Indian climates
7. Corrugated Bubble Wrap
This eco-alternative to plastic bubble wrap is made by embossing or fluting kraft paper to create cushioning. It’s biodegradable, recyclable, and just as effective in shock absorption for fragile goods.
- Common Uses: Electronics, glassware, home décor shipping
- Why It Works: Strong yet flexible, easy to store, and suitable for all sizes of packaging
- Pro Tip: Combine with water-activated tape for a 100% plastic-free package
8. Mushroom Packaging
Mushroom packaging is created by growing mycelium (the root structure of fungi) around agricultural waste to form custom molds. This innovative material decomposes naturally and leaves no toxic residue behind.
- Common Uses: Premium electronics, glass bottles, cosmetic jars
- Why It Works: Shock-resistant, lightweight, and zero-waste
- Forward-Thinking Brands: Startups and D2C brands use this for a strong sustainability signal
Sustainable Doesn’t Have to Mean Complicated—We Make It Work
At Greenworksbio, we make the switch to eco-friendly packaging easier, not harder. Our CPCB-certified, compostable solutions—from PLA+PBAT-based courier bags and food trays to recyclable films and custom labels—are designed to work with India’s waste systems and your operational flow.
Backed by EN 13432, ISO 17088, and ASTM D6400 certifications, our packaging isn’t just sustainable—it’s scalable, compliant, and supply-chain ready. Connect with our team today for a tailored consultation and start using materials that meet both regulatory and real-world demands.
Conclusion
Choosing the right types of food packaging material is no longer just a logistics decision—it’s a brand decision. Materials like compostable bioplastics, molded pulp, and natural materials such as water-activated tape are more than green buzzwords—they’re real-world solutions adopted by forward-thinking brands.
Whether you’re aiming to reduce plastic, meet compliance, or offer a better unboxing experience, the raw materials you use in the packaging industry speak volumes. Use this guide to rethink your packaging choices and take the next step toward a sustainable, scalable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main challenges of transitioning to sustainable packaging in India?
Transitioning to sustainable packaging in India involves high costs, limited access to eco-friendly materials, and adapting existing supply chain systems. Balancing environmental impact and practicality is key for improving this shift.
How do I identify if a packaging material is eco-friendly?
Look for certifications or labels indicating sustainability and compostability. Check factors like recyclability and carbon footprint of the materials. Transparent details about the environmental impact help in identifying eco-friendly packaging.
Are bioplastics widely available in India?
Bioplastics are increasingly accessible in India, especially for industries requiring flexible and food-safe plastic packaging. Availability issues still arise due to dependency on imports and supply inconsistencies for varied products.
Can sustainable packaging be cost-effective for small businesses?
Yes, small businesses can adopt cost-effective, sustainable options by using recyclable or paper-based materials. Lower shipping costs and bulk purchases from reliable suppliers further support affordability without compromising quality.
Which packaging material has the highest recycling rate in India?
Paper-based materials, including cardboard boxes and paper bags, boast the highest recycling rate in India. Glass bottles also rank high due to their long-term usability in packaging operations.

